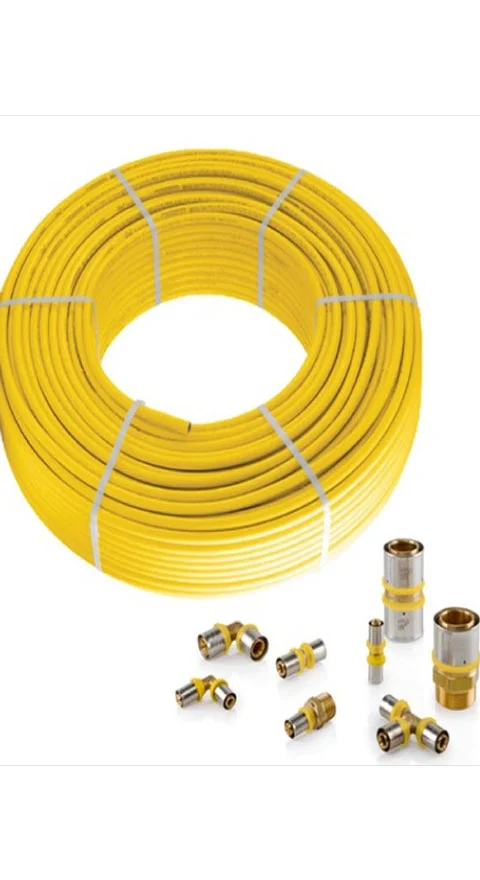
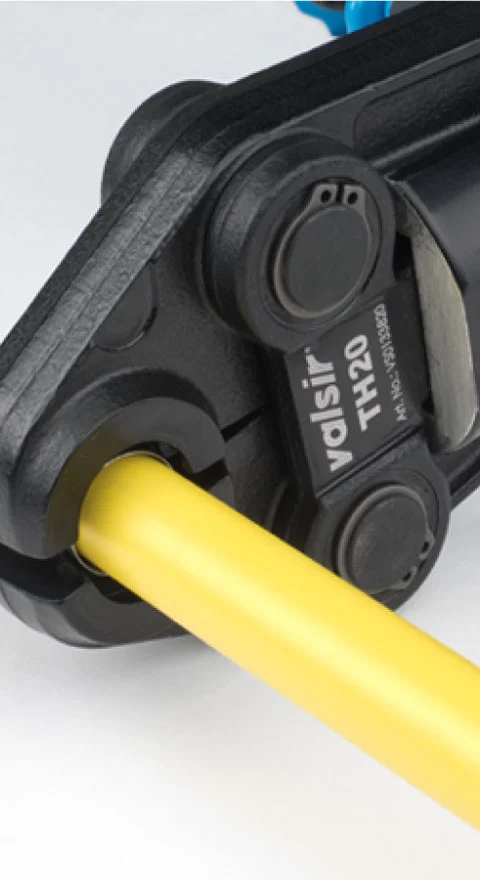
Plastic Pipes for LPG reticulation
Plastic pipes can be used for LPG (liquid petroleum gas) distribution, but they must meet certain requirements and standards. The most common types of plastic pipes used for LPG distribution are polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes.
Polyethylene (PE) pipes are suitable for use with LPG because they have good chemical resistance and can withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with LPG. They are also lightweight and easy to install, which makes them a popular choice for LPG distribution systems.
PVC pipes are also suitable for use with LPG, however, they have a limited temperature range and are not recommended for use in systems where the temperature exceeds 60°C. PVC pipes are also not as durable as PE pipes and are more prone to cracking and damage.
It's important to note that for both types of plastic pipes, the pipes and fittings must meet the relevant safety standards and must be properly installed and maintained to ensure safe and reliable operation.
It is also important to consider that LPG has a high vapor density than air, so it can accumulate in low-lying areas, that's why the LPG piping must be adequately ventilated.
Plastic Pipes for LPG
The two most common types of plastic pipes used for LPG (liquid petroleum gas) distribution are polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes.
- Polyethylene (PE) pipes: These pipes are made from a thermoplastic polymer and are suitable for use with LPG because they have good chemical resistance and can withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with LPG. They are also lightweight and easy to install, which makes them a popular choice for LPG distribution systems. They are available in different grades and thicknesses, such as PE80 and PE100.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes: These pipes are also made from a thermoplastic polymer and are suitable for use with LPG, however, they have a limited temperature range and are not recommended for use in systems where the temperature exceeds 60°C. PVC pipes are also not as durable as PE pipes and are more prone to cracking and damage. PVC pipes are available in different grades and thicknesses, such as uPVC, cPVC.
It's important to note that for both types of plastic pipes, the pipes and fittings must meet the relevant safety standards such as AS/NZS 1477:2013 and must be properly installed and maintained to ensure safe and reliable operation.